Delegate is a method or an object that refers to a method. A delegate provides a mean to encapsulate a method. A delegate holds a reference to a method and used to invoked the method.
Program of Delegate in Static Manner: Simple Console application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Delegates
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b, result;
Intops intop;
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter 2 integer");
Console.Write("a-");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("a-");
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("b-");
intop = new Intops(add);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Addition-" + result);
intop = new Intops(sub);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Substraction-" + result);
intop = new Intops(div );
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Division-" + result);
intop = new Intops(mul);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Multiplication-" + result );
Console.ReadLine();
}
delegate int Intops(int x, int y);
static int add(int a, int b)
{ return a + b;}
static int sub(int a, int b)
{ return a - b; }
static int div(int a, int b)
{ return a / b; }
static int mul(int a, int b)
{ return a * b; }
}
}
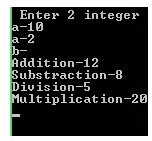
Output:
Program of Delegate in Instance Manner:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Delegate2
{
delegate int Intops(int a,int b);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b, result;
Intops intop;
Program p = new Program();
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter 2 integer");
Console.Write("a-");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("a-");
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("b-");
intop = p.add;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Addition-" + result);
intop = p.sub;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Substraction-" + result);
intop = p.div;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Division-" + result);
intop = p.mul;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Multiplication-" + result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public int add(int a, int b)
{ return a + b; }
public int sub(int a, int b)
{ return a - b; }
public int div(int a, int b)
{ return a / b; }
public int mul(int a, int b)
{ return a * b; }
}
}
Output:
output will be similar like above.
Program of Delegate in Static Manner: Simple Console application
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Delegates
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b, result;
Intops intop;
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter 2 integer");
Console.Write("a-");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("a-");
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("b-");
intop = new Intops(add);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Addition-" + result);
intop = new Intops(sub);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Substraction-" + result);
intop = new Intops(div );
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Division-" + result);
intop = new Intops(mul);
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Multiplication-" + result );
Console.ReadLine();
}
delegate int Intops(int x, int y);
static int add(int a, int b)
{ return a + b;}
static int sub(int a, int b)
{ return a - b; }
static int div(int a, int b)
{ return a / b; }
static int mul(int a, int b)
{ return a * b; }
}
}
Output:
Program of Delegate in Instance Manner:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace Delegate2
{
delegate int Intops(int a,int b);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a, b, result;
Intops intop;
Program p = new Program();
Console.WriteLine("\n Enter 2 integer");
Console.Write("a-");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("a-");
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("b-");
intop = p.add;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Addition-" + result);
intop = p.sub;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Substraction-" + result);
intop = p.div;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Division-" + result);
intop = p.mul;
result = intop(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("Multiplication-" + result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
public int add(int a, int b)
{ return a + b; }
public int sub(int a, int b)
{ return a - b; }
public int div(int a, int b)
{ return a / b; }
public int mul(int a, int b)
{ return a * b; }
}
}
Output:
output will be similar like above.
No comments:
Post a Comment